June 9, 2106 - Coronary artery calcium (CAC) scoring on top of myocardial perfusion imaging with single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) in patients suspected for coronary artery disease (CAD) is strongly encouraged based on the results of a recent study.1
Although not a well-established protocol, researchers evaluated 4899 symptomatic patients without a history of coronary artery disease referred for SPECT and CAC scoring. Major adverse cardiac events (MACEs) were defined as late revascularization (>90 days after scanning), nonfatal myocardial infarction, and all-cause mortality. The frequency of abnormal SPECT increased with higher CAC scores. A total of 278 MACEs were observed. The analysis showed both SPECT and CAC score were independent predictors of MACE.
The authors concluded CAC score and SPECT are independent predictors of MACE in patients suspected for coronary artery disease, and said they strongly support performing a CAC score in addition to SPECT in symptomatic patients to better define the risk of events during follow-up.
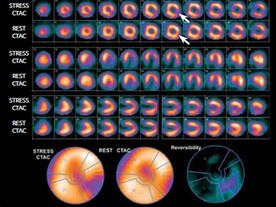
Figure: IQ•SPECT study shows reversible ischemia in the inferolateral wall (white arrows) suggestive of ischemia in the left circumflex artery territory.
References:
- Engbers E, Timmer J, Ottervanger JP, et al. Prognostic Value of Coronary Artery Calcium Scoring in Addition to Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomographic Myocardial Perfusion Imaging in Symptomatic Patients. American Heart Association, Inc. March 17, 2016.
- Single Vessel Coronary Artery Disease Evaluation. Siemens. http://usa.healthcare.siemens.com/molecular-imaging/case-studies/single-vessel-cad-evaluation-using-iq-spect.html.




