March 20, 2015 – Aspiration-related acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) frequently occurs in acute stroke patient with impairment consciousness, according to a study.
Aspiration of oral or gastric contents into the larynx and lower respiratory tract is a common problem in acute stroke patients, which significantly increases the incidence of ARDS, yet little is known about the clinical characteristics of aspiration-related ARDS in acute stroke patients. Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study on1495 consecutive patients with acute stroke over a 17-month period of time.
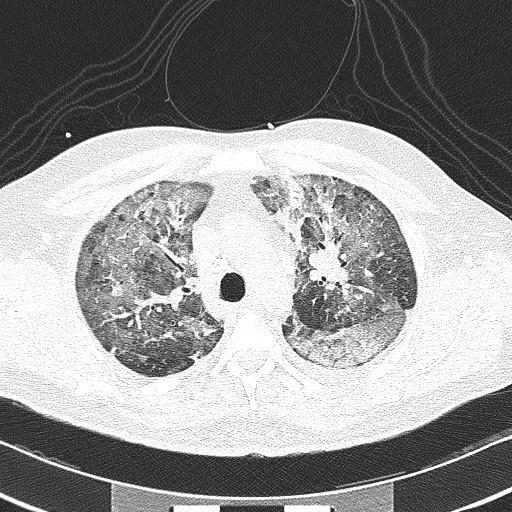
Source: RadRounds http://www.radrounds.com/photo/ards. Added by Dr Runalaila I Soofi on April 13, 2012.
Aspiration-related ARDS was diagnosed in 54 patients (3.6%). The most common presenting symptom was tachypnea (respiratory rate ≥25 breaths/min) in 50 cases. Computed tomography (CT) usually demonstrated diffuse ground-glass opacities (GGOs) and inhomogeneous patchy consolidations involving the low lobes. Age, NIHSS score, GCS score, dysphagia, dysarthria, hemoglobin concentration, serum aspertate aminotransferase (AST), serum albumin, serum sodium, and admission glucose level were independently associated with aspiration-related ARDS
The authors concluded that Aspiration-related ARDS frequently occurs in acute stroke patient with impairment consciousness, and suggested that performing chest CT timely in patients with ARDS may identify disease early and prompt treatment to save patients.




